FreeMarker (Template Engine)
Table of Contents
1. FreeMarker 简介
Apache FreeMarker is a template engine: a Java library to generate text output (HTML web pages, e-mails, configuration files, source code, etc.) based on templates and changing data.
FreeMarker 工作过程如图 1 所示。
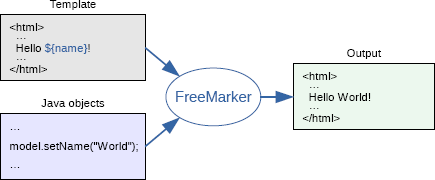
Figure 1: FreeMarker 工作过程
参考:
Apache FreeMarker Manual
Online FreeMarker Template Tester
1.1. 第一个 FreeMarker 程序
下面程序摘自:http://freemarker.org/docs/pgui_quickstart_all.html
首先,准备好模板文件(假设名为 test.ftlh):
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome ${user}!</h1>
<p>Our latest product:</p>
<a href="${latestProduct.url}">${latestProduct.name}</a>!
</body>
</html>
测试程序(准备数据,展开模板)如下:
import freemarker.template.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------------ */
/* You should do this ONLY ONCE in the whole application life-cycle: */
/* Create and adjust the configuration singleton */
Configuration cfg = new Configuration(Configuration.VERSION_2_3_25);
cfg.setDirectoryForTemplateLoading(new File("/where/you/store/templates"));
cfg.setDefaultEncoding("UTF-8");
cfg.setTemplateExceptionHandler(TemplateExceptionHandler.RETHROW_HANDLER);
cfg.setLogTemplateExceptions(false);
/* ------------------------------------------------------------------------ */
/* You usually do these for MULTIPLE TIMES in the application life-cycle: */
/* Create a data-model */
Map root = new HashMap();
root.put("user", "Big Joe");
Product latest = new Product();
latest.setUrl("products/greenmouse.html");
latest.setName("green mouse");
root.put("latestProduct", latest);
/* Get the template (uses cache internally) */
Template temp = cfg.getTemplate("test.ftlh");
/* Merge data-model with template */
Writer out = new OutputStreamWriter(System.out);
temp.process(root, out);
// Note: Depending on what `out` is, you may need to call `out.close()`.
// This is usually the case for file output, but not for servlet output.
}
}
其中,程序中使用的 Product 类,其定义如下:
/**
* Product bean; note that it must be a public class!
*/
public class Product {
private String url;
private String name;
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
运行上面测试程序,会输出下面内容(模板中 ${...} 内容被替换了,其它内容原封不动):
<html> <head> <title>Welcome!</title> </head> <body> <h1>Welcome Big Joe!</h1> <p>Our latest product:</p> <a href="products/greenmouse.html">green mouse</a>! </body> </html>
2. FreeMarker Template Language (FTL)
FreeMarker 模板可以看作是一个程序语言,被称为 FreeMarker Template Language (FTL)。
2.1. 模板文件基本组成
FreeMarker 模板文件主要由如下 4 个部分组成:
- 文本:直接输出的部分。
- 插值:格式为
${...}或#{...},它们将被替换为数据模型中的内容。 - 注释:模板中
<#--和-->之间的内容被认为是注释,FreeMarker 在产生输出文件时会删掉注释。 - FTL 指令(或称 FTL 标记):由 FreeMarker 指定,和 HTML 标记有点类似。一般,FTL 指令的名字以
#开头(用户可以自定义指令,名字以@开头),且不能嵌套在其它的不同指令中(同一个指令有的可以嵌套,如 if 指令)。这是<#if>指令的一个例子:<#if animals.python.price == 0>Pythons are free today!</#if>,只有当条件animals.python.price == 0为真时,才会输出“Pythons are free today!”。
注意:
- FTL 区分大小写,比如
${name}和${Name},以及${NAME}是相互不同的。 - “插值”只能出现在文本中(如
<h1>Hello ${name}!</h1>),或者字符串(如<#include "/footer/${company}.html">)中。这种用法:<#if ${big}>...</#if>(会导致语法错误)或者这种用法<#if "${big}">...</#if>(if 指令需要 boolean 值,但这里是 string,会导致运行时错误)都是错误的用法。对于这个例子,正确的写法为<#if big>...</#if>。 - 注释可以内嵌在 FTL 指令或者插值中。如:
${user <#-- The name of user -->}!</h1>是合法的写法。
2.2. FTL 指令(标记)
一般地,FTL 标记以“开始标记” <#directivename parameters> 开始,以“结束标记” </#directivename> 结尾;也有一些标记(如 <#include something> )只有“开始标记”,而没有“结束标记”(你也无需写为 <#include something /> ,因为 FreeMarker 知道 include 指令不需要结束标记)。
FreeMarker 允许用户自定义标记,用户自定义标记以 <@mydirective parameters> 开始,以 </@mydirective> 结尾;如果用户自定义标记不需要嵌套内容,则应用写为 <@mydirective parameters /> ,这类似于 xml 标记 <img ... /> 。
2.2.1. 指令:assign
使用 assign 指令可以创建一个新变量,或者替换一个存在的变量。其基本形式为:
<#assign name1=value1 name2=value2 ... nameN=valueN>
2.2.2. 指令:function, return
使用 function 指令可以创建函数。语法为:
<#function name param1 param2 ... paramN> ... <#return returnValue> ... </#function>
如,有下面模板:
<#function avg x y>
<#return (x + y) / 2>
</#function>
${avg(2, 3)}
模板展开后会输出:
2.5
2.2.3. 指令:if
if 指令是一个常用的分支控制指令。语法如下:
<#if condition> ... <#elseif condition2> ... <#elseif condition3> ... ... <#else> ... </#if>
其中, elseif 部分和 else 部分都是可选的。
if 指令可以嵌套使用。如:
<#if x == 1>
x is 1
<#if y == 1>
and y is 1 too
<#else>
but y is not
</#if>
<#else>
x is not 1
<#if y < 0>
and y is less than 0
</#if>
</#if>
if 指令使用实例:
<#assign x=2> <#if x == 1> x is 1 <#elseif x == 2> x is 2 <#elseif x == 3> x is 3 </#if>
上面模板展开后会输出:
x is 2
2.2.4. 指令:include
可以使用 include 指令把另外一个模板插入到当前模板中,其语法为:
<#include path options>
其中,path 为另外一个模板的路径,option 是可选的。
例如,文件/common/copyright.ftl 的内容为:
Copyright 2001-2002 ${me}<br>
All rights reserved.
有下面模板:
<#assign me = "Juila Smith"> <h1>Some test</h1> <p>Yeah. <hr> <#include "/common/copyright.ftl">
模板展开后会输出:
<h1>Some test</h1> <p>Yeah. <hr> Copyright 2001-2002 Juila Smith All rights reserved.
2.2.5. 指令:list, else, items, sep, break
list 指令用于迭代输出数据模型中的集合。
下面是 list 指令的基本形式(这里称为形式一):
<#list sequence as item>
Part repeated for each item
<#else>
Part executed when there are 0 items
</#list>
其中, else 部分可以省略;item 可取任意名字,代表被迭代输出的集合元素。
比如,有下面模板:
<#list ['Joe', 'Kate', 'Fred'] as user>
<p>${user}
</#list>
模板展开后会输出:
<p>Joe <p>Kate <p>Fred
list 指令可以嵌套使用。如,有下面模板:
<#list 1..2 as i>
<#list 1..3 as j>
i = ${i}, j = ${j}
</#list>
</#list>
模板展开后会输出:
i = 1, j = 1
i = 1, j = 2
i = 1, j = 3
i = 2, j = 1
i = 2, j = 2
i = 2, j = 3
2.2.5.1. items 指令
下面是 list 指令的另一种形式(这里称为形式二):
<#list sequence>
Part executed once if we have more than 0 items
<#items as item>
Part repeated for each item
</#items>
Part executed once if we have more than 0 items
<#else>
Part executed when there are 0 items
</#list>
比如,有下面模板:
<#list ['Joe', 'Kate', 'Fred']>
<ul>
<#items as user>
<li>${user}</li>
</#items>
</ul>
<#else>
<p>No users
</#list>
模板展开后会输出:
<ul>
<li>Joe</li>
<li>Kate</li>
<li>Fred</li>
</ul>
2.2.5.2. sep 指令
sep is used when you have to display something between each item (but not before the first item or after the last item).
比如,有下面模板:
<#list ['Joe', 'Kate', 'Fred'] as user>${user}<#sep>, </#sep></#list>
模板展开后会输出:
Joe, Kate, Fred
2.2.5.3. break 指令
You can exit the iteration at any point with the break directive.
比如,有下面模板:
<#list 1..10 as x>
${x}
<#if x == 3>
<#break>
</#if>
</#list>
模板展开后会输出:
1 2 3
2.2.6. 指令:noparse
noparse 指令之间的内容会被 FreeMarker 原封不动地输出,其语法为:
<#noparse> ... </#noparse>
2.2.7. 指令:switch, case, default, break
FreeMarker 中 switch, case, default, break 指令,类似于 Java 的 switch 语句。语法如下:
<#switch value>
<#case refValue1>
...
<#break>
<#case refValue2>
...
<#break>
...
<#case refValueN>
...
<#break>
<#default>
...
</#switch>
3. Expressions
When you supply values for interpolations or directive parameters you can use variables or more complex expressions. Let's see some concrete examples:
- When you supply value for interpolations: The usage of interpolations is
${expression}where expression gives the value you want to insert into the output as text. For example${(5 + 8)/2}prints "6.5" to the output. - When you supply a value for the directive parameter: For example, the syntax of
ifdirective is:<#if expression>...</#if>. The expression here must evaluate to a boolean value. For example in<#if 2 < 3>the2 < 3(2 is less than 3) is an expression which evaluates to true.
3.1. 表达式及其实例
| Expression | Example |
|---|---|
| String | "Foo" or 'Foo' |
| Number | 123.45 |
| Bollean | true, false |
| Sequence | ["foo", "bar"] |
| Hash | {"name":"green mouse", "price":150} |
3.2. Built-in(?)
The so-called built-ins are like subvariables that aren't coming from the data-model, but added by FreeMarker to the values. In order to make it clear where subvariables comes from, you have to use ? (question mark) instead of . (dot) to access them.
不同类型的表达式,对应有不同的 built-in,可以通过问号 ? 来访问 built-in。
下面是一些常用 built-ins 的实例。比如,有下面模板:
${"hello freemarker"?upper_case}
${"hello freemarker"?cap_first}
${"hello freemarker"?length}
${["foo", "bar"]?size}
${["foo", "bar"]?join(", ")}
模板展开后会输出:
HELLO FREEMARKER Hello freemarker 16 2 foo, bar
3.3. 处理 null 值
如果 data model 中某值为 null,不能直接访问它,否则会把异常。假设 user 并没有在 data model 中定义,如果模板中有代码 ${user} ,则会报异常。
3.3.1. 测试表达式是否存在(??)
可以通过 unsafe_expr?? 或者 (unsafe_expr)?? 来测试表达式 unsafe_expr 是否为 null。
比如,有下面模板:
<#if mouse??> Mouse found <#else> No mouse found </#if> Creating mouse... <#assign mouse = "Jerry"> <#if mouse??> Mouse found <#else> No mouse found </#if>
模板展开后会输出:
No mouse found Creating mouse... Mouse found
3.3.2. 表达式默认值(!)
当表达式为 null 时,我们可以为它指定默认值。为表达式 unsafe_expr 指定默认值为 default_expr 的写法为: unsafe_expr!default_expr 或者 (unsafe_expr)!default_expr 。
比如,有下面模板:
${mouse!"No mouse."}
<#assign mouse="Jerry">
${mouse!"No mouse."}
模板展开后会输出:
No mouse. Jerry
4. 自定义指令
FreeMarker 中可以自定义指令。 和内置指令以 # 开头不同,自定义指令以 @ 开头。
参考:
Defining your own directives: http://freemarker.org/docs/dgui_misc_userdefdir.html
4.1. 用 macro 指令自定义指令
用 macro 指令可以自定义指令。
比如,有下面模板:
<#macro test> This is test text </#macro> <#-- call the macro: --> <@test/> <@test/>
模板展开后会输出:
This is test text This is test text
再看一个带参数的例子。比如,有下面模板:
<#macro test foo bar baaz>
Test text, and the params: ${foo}, ${bar}, ${baaz}
</#macro>
<#-- call the macro: -->
<@test foo="a" bar="b" baaz=5*5-2/>
<@test foo="x" bar="y" baaz=10/>
模板展开后会输出:
Test text, and the params: a, b, 23 Test text, and the params: x, y, 10
4.2. 在 Java 中自定义指令
在 Java 中自定义指令需要实现 freemarker.template.TemplateDirectiveModell 接口。简单例子,可参考:http://freemarker.org/docs/pgui_datamodel_directive.html
5. Miscellaneous
5.1. Auto-escaping and output formats
当我们用 FreeMarker 生成 HTML 文件时,假设模板中有 ${name}$ ,而程序中 name 的值为 Someone & Co. ,在 HTML 中,它的正确输出其实应该是 Someone & Co. 。通过配置,可以让 FreeMarker 帮我们进行自动转义。
方法一:
The recommended practice is using "ftlh" file extension to activate HTML auto-escaping, and "ftlx" file extension to activate XML auto-escaping.
方法二:
在模板文件的第一行用 ftl 指令设置输出格式,如:
<#ftl output_format="HTML">
下面是一些内置的 output format:
| Name | Description | MIME Type | Default implementation |
|---|---|---|---|
| HTML | Escapes <, >, &, ", ' as <, >, &, ", ' | text/html | HTMLOutputFormat.INSTANCE |
| XHTML | Escapes <, >, &, ", ' as <, >, &, ", ' | application/xhtml+xml | XHTMLOutputFormat.INSTANCE |
| XML | Escapes <, >, &, ", ' as <, >, &, ", ' | application/xml | XMLOutputFormat.INSTANCE |
| RTF | Escapes {, }, \ as \{, \}, \\ |
application/rtf | RTFOutputFormat.INSTANCE |
| undefined | Doesn't escape. The default output format. | None (null) | UndefinedOutputFormat.INSTANCE |
5.1.1. 指令:outputformat
使用指令 outputformat 可以强制改变“输出格式”。其语法为:
<#outputformat formatName> ... </#outputFormat>
比如,有下面模板:
<#assign mo1 = "Foo's bar {}">
HTML: <#outputformat 'HTML'>${mo1}</#outputformat>
XML: <#outputformat 'XML'>${mo1}</#outputformat>
RTF: <#outputformat 'RTF'>${mo1}</#outputformat>
模板展开后会输出:
HTML: Foo's bar {}
XML: Foo's bar {}
RTF: Foo's bar \{\}
5.1.2. 指令:noautoesc
使用指令 noautosec 可以临时禁止对输出的转义。
比如,有下面模板:
<#ftl output_format="HTML">
${"&"}
${"<"}
<#noautoesc>
${"&"}
${"<"}
</#noautoesc>
${"&"}
${"<"}
模板展开后会输出:
& < & < & <