Mnemonic and HD Wallet
Table of Contents
1. Mnemonic(BIP39)
比特币私钥难于记忆和保管。后来人们提出了下面思路来产生私钥:
助记词 -> Seed (512-bits) -> 私钥
\________ ________/ \________ _________/
\/ \/
BIP39 BIP32/BIP44
由“助记词(Mnemonic)”推导出 Seed,再由 Seed 推导出私钥。这样,我们只需要备份“助记词(Mnemonic)”,需要私钥时,再由助记词推导出私钥即可。
1.1. 生成 Mnemonic
BIP39 包含两部分内容,一是如何生成 Mnemonic,二是如何转换 Mnemonic 为 Seed。这一节介绍如何生成 Mnemonic。
生成 Mnemonic 的算法(如图 1 所示)如下:
- 生成一个长度为 128~256 位(bits)的随机序列(熵);
- 取熵的 SHA256 哈希后的前 n 位作为校验和(n=熵长度/32);
- 随机序列 + 校验和;
- 把步骤 3 得到的结果按“每 11 位”进行切割;
- 步骤 4 得到的每 11 位字节匹配词库(英文词库 https://github.com/bitcoin/bips/blob/master/bip-0039/english.txt )的一个词。注:11 个比特位全部为 0(或者全部为 1)时得到最小(或者最大)编号 0(或者 2047),所以词库只要 2048 个单词就足够了;
- 步骤 5 得到的结果就是助记词。

Figure 1: 生成 Mnemonic 的算法(以 128 位熵为例)
由于熵的比特位长度是 128~256,得到的助记词个数会为 12/15/18/21/24,如表 1 所示。
| Entropy (bits) | Checksum (bits) | Entropy + checksum (bits) | Mnemonic length (words) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 128 | 4 | 132 | 12 |
| 160 | 5 | 165 | 15 |
| 192 | 6 | 198 | 18 |
| 224 | 7 | 231 | 21 |
| 256 | 8 | 264 | 24 |
1.1.1. Mnemonic 生成实例
下面以随机生成 128 位熵为例介绍一下 Mnemonic 的生成过程。
- 生成 128 位的随机序列(熵),如
bb5a11f83e9a54c8b14c1394f970c1d2; - SHA256 为
f4780ebd78294dbf1972ef1c7d9c4e470b4c5755d3cdf202510e4148f7ba315c,取前 4 位(即f)作为校验和; 随机序列(熵)和校验和拼接在一起,得到
bb5a11f83e9a54c8b14c1394f970c1d2f,如果表示为二进制就是:
101110110101101000010001111110000011111010011010010101001100100010110001010011000001001110010100111110010111000011000001110100101111
把步骤 3 得到的结果按“每 11 位”进行切割,得到:
10111011010 11010000100 01111110000 01111101001 10100101010 01100100010 11000101001 10000010011 10010100111 11001011100 00110000011 10100101111
把这个列表转换为 10 进行,从词库中找到对应下标(首个下标从 0 开始)的单词,分别为“robust spatial lawn large pipe gold share list neutral slide corn planet”。
- 助记词就是“robust spatial lawn large pipe gold share list neutral slide corn planet”。
1.1.2. 讲究的词库
词库中一共有 2048 个单词。BIP39 规定了下面 3 个要求:
- 只使用前 4 个字母就可以无歧义地找到某个单词,即词库不中存在前 4 个字母相同的多个单词;
- 避免包含相似的词,比如不会同时包含单词“woman”和“women”;
- 词库本身排序。
1.2. 转换 Mnemonic 为 512-bit Seed
使用 PBKDF2(这是一种 Key stretching 算法)转换 Mnemonic 为 512-bit Seed,如图 2 所示。
PBKDF2 的各个参数如下:
- 助记词句子(中间用英文空格分开)作为 PBKDF2 函数的密码参数;
- "mnemonic" + passphrase 作为 PBKDF2 函数的盐参数,其中 passphrase 可为空;
- 重复计算的次数为 2048;
- 输出长度为 64 字节(512 比特位)。

Figure 2: 转换 Mnemonic 为 Seed
详情可参考节 7.1 中的函数 mnemonic_to_bip39seed 。
2. HD Wallet(BIP32)
有了 Seed 后,可以利用分层确定性(Hierarchical Deterministic,HD)钱包规范(BIP32)来推导出无数个私钥了。分为两个过程:一是转换 Seed 为主私钥和主链码,二是子私钥推导。
2.1. 转换 Seed 为主私钥和主链码
2.2. 子私钥推导
BIP32 子私钥推导如图 4 所示,可以一直进行下去,每推导一次只需要额外提供一个 index 值。
Figure 4: BIP32 derive private child key
从图中可知,推导函数的输入有 3 个,而输出有 2 个。前一节求得的 master private key 和 master chain code 分别作为 private key 0 和 chain code 0 再指定一个 index 就可以开始推导了。
2.2.1. Non-Hardened 推导实例
Non-Hardened Derivation 的具体细节如图 5 所示,上子图是从 parent private key 推导 child private key;下子图是从 parent public key 推导 child public key。

Figure 5: BIP32 Non-Hardened Derivation
下面演示一下,采用 Non-Hardened Derivation 方式,如何从 parent private key 推导 child private key。
假设:
parent private key = 0xca0fb280fc4f60b39fe8bd080647ccbc8d983352ad398bb2dd17e3187a29cc54 chain_code = 0xa16145b061cd56dcbcadfb2bc9e1e8215cc392133117ebdc2ca970b63e0f9e3f index = 0
先计算出父私钥 0xca0fb280fc4f60b39fe8bd080647ccbc8d983352ad398bb2dd17e3187a29cc54 对应的压缩格式公钥,为 0x0204dff2751093a38752923e8980dc004fabc35e02c2238e2cb32d4cebc696614c,然后这个压缩格式公钥和 index(按 4 字节序列化)连接在一起组成 HMAC-SHA512 的 Data:
0204dff2751093a38752923e8980dc004fabc35e02c2238e2cb32d4cebc696614c00000000
\_____________________________ _________________________________/\__ __/
\/ \/
compressed public key index
而 chain_code 作为 HMAC-SHA512 的 Key,HMAC-SHA512 结束后,得到 512 bits:
import hashlib
import hmac
secretKey = bytes.fromhex('a16145b061cd56dcbcadfb2bc9e1e8215cc392133117ebdc2ca970b63e0f9e3f')
data = bytes.fromhex('0204dff2751093a38752923e8980dc004fabc35e02c2238e2cb32d4cebc696614c00000000')
out = hmac.new(secretKey, data, hashlib.sha512).hexdigest()
print(out) # 55d46a0a07653bb49488b368f05ab72e465c0c1b797eef5a8dacc549e96a0515d5582fd555c4518ce240c8e5e4037003e7807692c84eba08fb16296a9f92230a
左边 256 bits 0x55d46a0a07653bb49488b368f05ab72e465c0c1b797eef5a8dacc549e96a0515 记为
$ python3 Python 3.11.3 >>> (0x55d46a0a07653bb49488b368f05ab72e465c0c1b797eef5a8dacc549e96a0515 + 0xca0fb280fc4f60b39fe8bd080647ccbc8d983352ad398bb2dd17e3187a29cc54) % 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFEBAAEDCE6AF48A03BBFD25E8CD0364141 14424736433571262452967532751661889042251919337314428124287966680328519389224 >>> hex(14424736433571262452967532751661889042251919337314428124287966680328519389224) '0x1fe41c8b03b49c6834717070f6a283ec19456287776fdad1aaf249d5935d9028'
右边 256 bits 0xd5582fd555c4518ce240c8e5e4037003e7807692c84eba08fb16296a9f92230a 就是下一个 chain_code。
所以,最终我们得到的 parent private key 和下一个 chain_code 为:
parent private key = 0x1fe41c8b03b49c6834717070f6a283ec19456287776fdad1aaf249d5935d9028 chain_code = 0xd5582fd555c4518ce240c8e5e4037003e7807692c84eba08fb16296a9f92230a
2.2.2. Hardened 推导实例
Hardened Derivation(index 必须大于等于 0x80000000)的具体细节如图 6 所示,红色部分是和 Non-Hardened 推导不相同的地方。

Figure 6: BIP32 Hardened Derivation
下面演示一下,采用 Hardened Derivation 方式,如何从 parent private key 推导 child private key。
假设:
parent private key = 0xb36aa6163f909cbf8941937f0636e9c5ee255da9c1df6cc5f706ad2e8fb2306c chain_code = 0xb5f06c04b094b533cf0726f9efcf7ffd90027a8c979e88bfd6fabeab15274184 index = 44' # 十六进制 2c,有个单引号表示它是 Hardened Derivation,需要再加上 0x80000000,就是 0x8000002c
下面按图 6 的规定拼凑出 HMAC-SHA512 的 Data:
00b36aa6163f909cbf8941937f0636e9c5ee255da9c1df6cc5f706ad2e8fb2306c8000002c
\/\_____________________________ _______________________________/\__ __/
\/ \/
pad parent private key index
而 chain_code 作为 HMAC-SHA512 的 Key,HMAC-SHA512 结束后,得到 512 bits:
import hashlib
import hmac
secretKey = bytes.fromhex('b5f06c04b094b533cf0726f9efcf7ffd90027a8c979e88bfd6fabeab15274184')
data = bytes.fromhex('00b36aa6163f909cbf8941937f0636e9c5ee255da9c1df6cc5f706ad2e8fb2306c8000002c')
out = hmac.new(secretKey, data, hashlib.sha512).hexdigest()
print(out) # 2709119db0e0ed8141d4679976040b4ca7b38f96f29625d4e9209d10e6432bb375febca09aa2c681f2ea22f364cff82fbc7cea8ae7f102411a798b90f58fca17
左边 256 bits 0x2709119db0e0ed8141d4679976040b4ca7b38f96f29625d4e9209d10e6432bb3 记为
$ python3 Python 3.11.3 >>> (0x2709119db0e0ed8141d4679976040b4ca7b38f96f29625d4e9209d10e6432bb3 + 0xb36aa6163f909cbf8941937f0636e9c5ee255da9c1df6cc5f706ad2e8fb2306c) % 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFEBAAEDCE6AF48A03BBFD25E8CD0364141 98808656274335160624786688486525798401691562863050131271609462243034020535327 >>> hex(14424736433571262452967532751661889042251919337314428124287966680328519389224) '0xda73b7b3f0718a40cb15fb187c3af51295d8ed40b475929ae0274a3f75f55c1f'
右边 256 bits 0x75febca09aa2c681f2ea22f364cff82fbc7cea8ae7f102411a798b90f58fca17 就是下一个 chain_code。
所以,最终我们得到的 child private key 和下一个 chain_code 为:
child private key = 0xda73b7b3f0718a40cb15fb187c3af51295d8ed40b475929ae0274a3f75f55c1f chain_code = 0x75febca09aa2c681f2ea22f364cff82fbc7cea8ae7f102411a798b90f58fca17
2.2.3. Non-Hardened VS. Hardened Derivation
对于 Non-Hardened Derivation 钱包有个特点:指定 index 后,从父公钥可以直接推导出子公钥,具体方法可参考:https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/BIP_0032#Public_parent_key_.E2.86.92_public_child_key ,推导函数的细节可参考节 7.1 中的函数 derive_bip32childkey 。这意味着: 不需要使用父私钥的情况下,可以生成很多受父私钥控制的钱包地址。 下面是这个特性的一个使用场景:某个商场的经理可以为大量客户每人生成一个付款地址,而这个过程中经理根本不用接触私钥。
我们知道“父私钥”和“子私钥”之间有一个偏移量(这个偏移量就是节 2.2.1 中的
不过 Non-Hardened Derivation 有个安全问题:从“parent extended public key”(所谓“父扩展公钥”就是父公钥和 chain code 两个数据的组合)和“子私钥”可反推出“父私钥”。 产生这个安全问题的原因是:我们可以找到了上面提到的这个偏移量,从而可以从子私钥直接得到父私钥了。相关实现可参考:https://github.com/BlockIo/multimerchant-python/blob/master/multimerchant/wallet/bip32.py#L384
注:对“父扩展公钥”的保存需要更加小心,不能像“父公钥”一样可以直接公开。因为“父扩展公钥”中还有另一个重要数据:chain code,有了 chain code 后就可以计算出偏移量。有了偏移量就可以从子私钥推导父私钥。
对于 Non-Hardened Derivation 来说,计算偏移量的具体方法是先计算 HMAC-SHA512(Key=chain code, Data=parent_pubkey||index) ,其结果的左边 256 比特位就是这个偏移量。而对于 Hardened Derivation 来说,由于不知道父私钥,所以无法计算出 HMAC-SHA512(Key=chain code, Data=0x00||parent_private_key||index),从而无法计算出这个偏移量,从而即使泄露了子私钥也无法推导出父私钥。
人们意识到了这个问题, 引入了 Hardened Derivation(即 index 大于等于 0x80000000 )来规避这个安全问题,所以为安全起见我们应该使用 Hardened Derivation。对于 Hardened Derivation 来说,推导子公钥时需要访问其父私钥。
Non-Hardened Derivation 和 Hardened Derivation 各有优缺点,如表 2 所示。
| 安全性 | 推导子钱包地址时是否需要访问父私钥 | |
|---|---|---|
| Non-Hardened Derivation | 不好。从“父扩展公钥和子私钥”可反推出“父私钥” | 否。从“父扩展公钥”即可推导“子公钥”,更便利 |
| Hardened Derivation | 好 | 是。需要“父私钥”参与才能推导“子公钥” |
3. Index 值规定(BIP44)
BIP44 规定了每次推导时使用的 index 值,这些 index 串起来(使用 / 做分隔符,最前面有个固定的 m )就是 path。BIP44 的 path 规范为:
m / purpose' / coin_type' / account' / change / address_index
注:
- m:This denotes that the path is rooted at the master key;
- purpose: Always set to 44 for BIP44 compliant wallets;
- coin_type:用于区分不同的币种,关于已注册的 coin_type,可参考:SLIP-0044 : Registered coin types for BIP-0044
- account:表示账户索引,从 0 开始;
- change:为 0 表示“接收”地址(外部地址),为 1 表示“找零”地址(内部地址);
- address_index:表示地址索引,从 0 开始。
如 BTC 的 path 为 m/44'/0'/0'/0/0 ,表示一共有 5 次推导,依次使用的 index 如表 3 所示。
| index | index (hex) | |
|---|---|---|
| 44' | 0x8000002c | purpose' |
| 0' | 0x80000000 | coin_type' |
| 0' | 0x80000000 | account' |
| 0 | 0x00 | change |
| 0 | 0x00 | address_index |
如果 index 记号中有 ' ,则表示 Hardened Derivation, 对应 index 额外加上 0x80000000 即可,如 44' 表示 0x8000002c (44 的 16 进制是 0x2c )。
推导函数的细节可参考节 7.1 中的函数 derive_bip32childkey 。
3.1. Other Derivation Scheme(BIP49/BIP84/BIP86)
使用 BIP44 可以从助记词推导出以 1 开头的普通 BTC 地址。如果要从助记词推导出“隔离见证兼容地址”可参考 BIP49;如果要从助记词推导出“隔离见证原生地址”可参考 BIP84;如果要从助记词推导出“Taproot 地址”可参考 BIP86。
参考:
BIP49 - Derivation scheme for P2WPKH-nested-in-P2SH based accounts
BIP84 - Derivation scheme for P2WPKH based accounts
BIP86 - Key Derivation for Single Key P2TR Outputs
4. 一组助记词推导多组助词词(BIP85)
如果助记词比较很多,那么备份管理助记词也比较麻烦。BIP85 中提出了由一个助记词推导多组助词词的方案,如图 7(摘自:https://airgapit.medium.com/secure-mnemonic-management-with-bip85-9af386159657 )所示。这样 我们只需要备份下主助记词就行了。 某个子助记词泄露了,不会影响到其它的助记词。
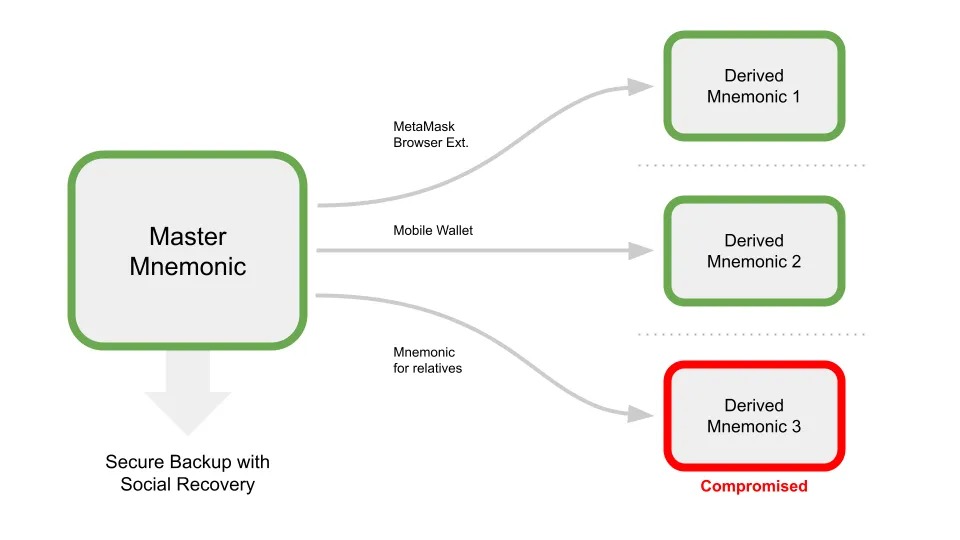
Figure 7: BIP85
支持 BIP85 的硬件钱包有 COLDCARD、Blockstream Jade 等。
5. 门限钱包对 BIP32 的支持
前面提到 BIP32 有两类推导方式:Non-Hardened Derivation 和 Hardened Derivation。
由于 Non-Hardened Derivation 不需要 Parent Private Key 的参与,门限钱包支持 Non-Hardened Derivation 相对比较简单(参考 tss-lib BIP-32 integration)。各个参与者在 Keygen 过程中约定好一个相同的 Chain Code,指定 Index 后,各个参与者可以本地计算出 HMAC-SHA512 的结果了。门限钱包 BIP32 Non-Hardened Derivation 的实现可参考 Binance 的 tss-lib 库和 Taurus 的 multi-party-sig 库。
门限钱包支持 Hardened Derivation 则比较麻烦,因为在进行 Hardened Derivation 时,计算 HMAC-SHA512 时需要 Parent Private Key 作为输入数据,而各个参与者手头并没有 Parent Private Key。一个显而易见的思路是使用通用 MPC 技术(如 GMW)来实现 HMAC-SHA512 的多方安全计算,而不泄露秘密输入,不过它的效率不高(摘自:BIP32-Compatible Threshold Wallets, 4.2 Hardened Node Derivation):
One obvious (and to the best of our knowledge the only) way to resolve the above issues is using generic multi-party computation (MPC) techniques [GMW87, Gol04, CCD88], which allow to securely compute any function in a distributed setting without revealing the function inputs. However, generic MPC is inherently inefficient, in particular since the BIP32 standard uses the well-known hash function SHA-512, which is known to be only inefficiently computable via MPC [BST21].
门限钱包 BIP32 Hardened Derivation 的实现可参考 AMIS 的 HTSS 库(它是一个 2-party Hardened Derivation,相关论文为 A Two-Party Hierarchical Deterministic Wallets in Practice)和 Unbound Security 的 blockchain-crypto-mpc 库。
由于门限钱包要支持 BIP32 Hardened Derivation 比较麻烦且效率不高,论文 BIP32-Compatible Threshold Wallets 中提出了利用 Threshold Verifiable Random Function (TVRF) 来实现 BIP32 类似效果的方案(不兼容 BIP32),这里不详细介绍。
6. Shamir's Secret-Sharing for Mnemonic Codes(SLIP39)
我们知道,利用 Shamir's Secret-Sharing 可以把一个私钥分散保存到
我们可以使用类似的思路把一组助记词保存到
支持 SLIP39 的硬件钱包有 Trezor Model T、Keystone。
7. 附录
7.1. 从 Mnemonic 生成 BTC 私钥(Python 实现)
下面 Python 程序可以从 Mnemonic(以“robust spatial lawn large pipe gold share list neutral slide corn planet”为例)生成 BTC 私钥:
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import hashlib
import hmac
import struct
from ecdsa.curves import SECP256k1
from ecdsa.ellipticcurve import Point, PointJacobi
BIP39_PBKDF2_ROUNDS = 2048
BIP39_SALT_MODIFIER = "mnemonic"
BIP32_PRIVDEV = 0x80000000
BIP32_CURVE = SECP256k1
BIP32_SEED_MODIFIER = b'Bitcoin seed' # https://en.bitcoin.it/wiki/BIP_0032
LEDGER_ETH_DERIVATION_PATH = "m/44'/0'/0'/0/0"
# bip44 define 5 levels in BIP32 path: m / purpose' / coin_type' / account' / change / address_index
# for bip44, purpose = 44
# for eth, coin_type = 60
# Registered coin types for BIP-0044, see https://github.com/satoshilabs/slips/blob/master/slip-0044.md
def pubkey_compressed_to_uncompressed(compressed_pubkey: bytes) -> bytes:
# modulo p which is defined by secp256k1's spec
p = 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFEFFFFFC2F
x = int.from_bytes(compressed_pubkey[1:33], byteorder='big')
y_sq = (pow(x, 3, p) + 7) % p
y = pow(y_sq, (p + 1) // 4, p)
if compressed_pubkey[0] % 2 != y % 2:
y = p - y
y = y.to_bytes(32, byteorder='big')
return b'\04' + compressed_pubkey[1:33] + y # x + y
def pubkey_from_bytes_to_point(pubkey: bytes) -> tuple[int, int]:
assert len(pubkey) == 33 or len(pubkey) == 65
if len(pubkey) == 33: # compressed pubkey
uncompressed_pubkey = pubkey_compressed_to_uncompressed(pubkey)
else:
uncompressed_pubkey = pubkey
x = int.from_bytes(uncompressed_pubkey[1:33], byteorder='big') # uncompressed_pubkey must contain prefix b'\04'
y = int.from_bytes(uncompressed_pubkey[33:65], byteorder='big')
return x, y
def pubkey_from_point_to_bytes(x: int, y: int, compressed: bool = True) -> bytes:
xstr = x.to_bytes(32, byteorder='big')
ystr = y.to_bytes(32, byteorder='big')
if compressed:
parity = y & 1
return (2 + parity).to_bytes(1, byteorder='big') + xstr
else:
return b'\04' + xstr + ystr
def prikey_to_pubkey(private_key: bytes, compressed_pubkey: bool = True) -> bytes:
Q: PointJacobi = int.from_bytes(private_key, byteorder='big') * SECP256k1.generator
return pubkey_from_point_to_bytes(Q.x(), Q.y(), compressed_pubkey)
def mnemonic_to_bip39seed(mnemonic: str, passphrase: str = "") -> bytes:
""" BIP39 seed from a mnemonic key.
Logic adapted from https://github.com/trezor/python-mnemonic. """
mnemonic = bytes(mnemonic, 'utf8')
salt = bytes(BIP39_SALT_MODIFIER + passphrase, 'utf8')
return hashlib.pbkdf2_hmac('sha512', mnemonic, salt, BIP39_PBKDF2_ROUNDS)
def bip39seed_to_bip32masternode(seed: bytes) -> tuple[bytes, bytes]:
""" BIP32 master node derivation from a bip39 seed.
Logic adapted from https://github.com/satoshilabs/slips/blob/master/slip-0010/testvectors.py. """
h = hmac.new(BIP32_SEED_MODIFIER, seed, hashlib.sha512).digest()
key, chain_code = h[:32], h[32:]
return key, chain_code
def derive_bip32childkey(parent_key: bytes, parent_chain_code: bytes, index: int) -> tuple[bytes, bytes]:
""" Derives a child key from an existing key, index is current derivation parameter.
Support:
1. parent private key -> child private key, in this case, parent_key must be 32 bytes
2. parent public key -> child public key, in this case, parent_key must be 33 bytes, index must < 0x80000000
"""
assert len(parent_key) == 32 or len(parent_key) == 33
assert len(parent_chain_code) == 32
parent_is_public_key = len(parent_key) == 33
if parent_is_public_key:
if (index & BIP32_PRIVDEV) != 0: # index >= 0x80000000, hardened child
raise Exception("hardened derivation is only defined for private key derivation, "
"not defined for public key derivation")
else: # normal public child
msg = parent_key
else:
if (index & BIP32_PRIVDEV) != 0: # index >= 0x80000000, hardened child
msg = b'\x00' + parent_key
else: # normal private child
msg = prikey_to_pubkey(parent_key) # get compressed public key from a private key
msg = msg + struct.pack('>L', index) # `>` means big-endian, `L` means unsigned long
# compute sha512
h = hmac.new(parent_chain_code, msg, hashlib.sha512).digest()
left32, chain_code = h[:32], h[32:]
a = int.from_bytes(left32, byteorder='big')
b = int.from_bytes(parent_key, byteorder='big')
if parent_is_public_key:
# build Point from compressed public key
x, y = pubkey_from_bytes_to_point(parent_key)
parent_public_key: Point = Point(BIP32_CURVE.curve, x, y)
# child_public_key = left32 * G + parent_public_key
child_public_key: PointJacobi = a * BIP32_CURVE.generator + PointJacobi.from_affine(parent_public_key)
if a >= BIP32_CURVE.order:
raise Exception("left32 greater than or equal to the order, please use another index")
if child_public_key == 0:
raise Exception("resulting public key is the point at infinity, please use another index")
key = pubkey_from_point_to_bytes(child_public_key.x(), child_public_key.y()) # 33 bytes
else:
child_private_key = (a + b) % BIP32_CURVE.order
# check validation of resulting key
if a >= BIP32_CURVE.order:
raise Exception("left32 greater than or equal to the order, please use another index")
if child_private_key == 0:
raise Exception("resulting private key is zero, please use another index")
key = child_private_key.to_bytes(32, byteorder='big') # 32 bytes
return key, chain_code
def parse_derivation_path(str_derivation_path: str) -> list[int]:
""" Parses a derivation path such as "m/44'/60/0'/0" and returns
list of integers for each element in path. """
path = []
if str_derivation_path[0:2] != 'm/':
raise ValueError("Can't recognize derivation path. It should look like \"m/44'/60/0'/0\".")
for i in str_derivation_path.lstrip('m/').split('/'):
if "'" in i:
path.append(BIP32_PRIVDEV + int(i[:-1]))
else:
path.append(int(i))
return path
def mnemonic_to_private_key(mnemonic: str, str_derivation_path: str = LEDGER_ETH_DERIVATION_PATH,
passphrase: str = "") -> bytes:
""" Performs all convertions to get a private key from a mnemonic sentence, including:
BIP39 mnemonic to seed
BIP32 seed to master key
BIP32 child derivation of a path provided
Parameters:
mnemonic -- seed wordlist, usually with 24 words, that is used for ledger wallet backup
str_derivation_path -- string that directs BIP32 key derivation, defaults to path
used by ledger ETH wallet
"""
derivation_path = parse_derivation_path(str_derivation_path)
bip39seed = mnemonic_to_bip39seed(mnemonic, passphrase)
master_private_key, master_chain_code = bip39seed_to_bip32masternode(bip39seed)
private_key, chain_code = master_private_key, master_chain_code
for i in derivation_path:
private_key, chain_code = derive_bip32childkey(private_key, chain_code, i)
return private_key
# bip44 path: m / purpose' / coin_type' / account' / change / address_index
# For BTC:
# m/44'/0'/0'/0/0
# 44' -> 0x80000000 + 0x2c # decimal 44 = hex 0x2c
# 0' -> 0x80000000 + 0x00
# 0' -> 0x80000000 + 0x00
# 0 -> 0x00
# 0 -> 0x00
m = "robust spatial lawn large pipe gold share list neutral slide corn planet"
bip39seed = mnemonic_to_bip39seed(m)
private_key_0, chain_code_0 = bip39seed_to_bip32masternode(bip39seed)
private_key_1, chain_code_1 = derive_bip32childkey(private_key_0, chain_code_0, 0x8000002c) # 44'
private_key_2, chain_code_2 = derive_bip32childkey(private_key_1, chain_code_1, 0x80000000) # 0'
private_key_3, chain_code_3 = derive_bip32childkey(private_key_2, chain_code_2, 0x80000000) # 0'
private_key_4, chain_code_4 = derive_bip32childkey(private_key_3, chain_code_3, 0x00) # 0
private_key_5, chain_code_5 = derive_bip32childkey(private_key_4, chain_code_4, 0x00) # 0
print("private_key = 0x{}".format(private_key_5.hex()))
# private_key = 0x36b5ff6f7900ec5fe287f084df52ae8aa971e5e5cc8755b0278e6aa526afe669
得到的 BTC 原始私钥为 0x36b5ff6f7900ec5fe287f084df52ae8aa971e5e5cc8755b0278e6aa526afe669 ,如果转换为 WIF-compressed 格式就是 Ky44Y5EKSTUDfTyCzzhxCxCZ9JP5iF5Ejt9CH3QhJaPeaCLu9jEb 。
同一个 Mnemonic,如果要生成 ETH 的私钥,只需要改变 BIP44 的 path,即把 coin_type 改为 60(参考 https://github.com/satoshilabs/slips/blob/master/slip-0044.md )即可:
# private_key_2, chain_code_2 = parent_private_key_2_child_private_key(private_key_1, chain_code_1, 0x80000000) # 0' #### change to: private_key_2, chain_code_2 = parent_private_key_2_child_private_key(private_key_1, chain_code_1, 0x8000003c) # 60'
这时,得到的 ETH 的私钥为 0x2dfb4fc4780d9d9f4f9f2aedd00795e4cbe26d3ad359ce7967412d0f9984e5e5 。
8. 参考
大部分插图摘自:Mastering Bitcoin, 2nd Edition, 2017
BIP32 - Hierarchical Deterministic Wallets
BIP39 - Mnemonic code for generating deterministic keys
BIP44 - Multi-Account Hierarchy for Deterministic Wallets
BIP49 - Derivation scheme for P2WPKH-nested-in-P2SH based accounts
BIP84 - Derivation scheme for P2WPKH based accounts
BIP86 - Key Derivation for Single Key P2TR Outputs
Mnemonic Code Converter
BIP32-Compatible Threshold Wallets

